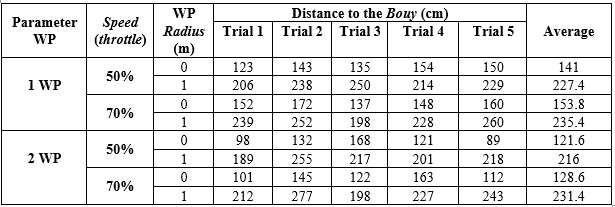
In the aspect of the seakeeping test, this ship is required to have the ability to maintain its stability in choppy water conditions properly. This test is conducted to meet IMO standards which limit the movement of ships due to waves that can cause motion sickness incidence. This test aims to maintain the position of the components attached to the ship such as sensors, GPS, cameras and other electrical components so that there is no change in position that causes malfunctions in the prototype system that can derail the mission on the trajectory due to the current waves on the water surface. In this research, a seakeeping test was carried out at a speed of 5 knots and 10 knots. The following is the data from the test results of the Mandakini Neo prototype ship maneuvering
After conducting several tests on the Mandakini Neo ship design, this ship design has a fairly small resistance value. The advantages of ships with small obstacles are that they can move forward and have good maneuverability, this is the strength of the ship in making it easier to maneuver to complete the mission. Basically, these obstacles are not only caused by external factors such as fluid and air. But it is also caused by various factors such as the designer's ability to select and create a model so that it is able to produce the smallest possible resistance.
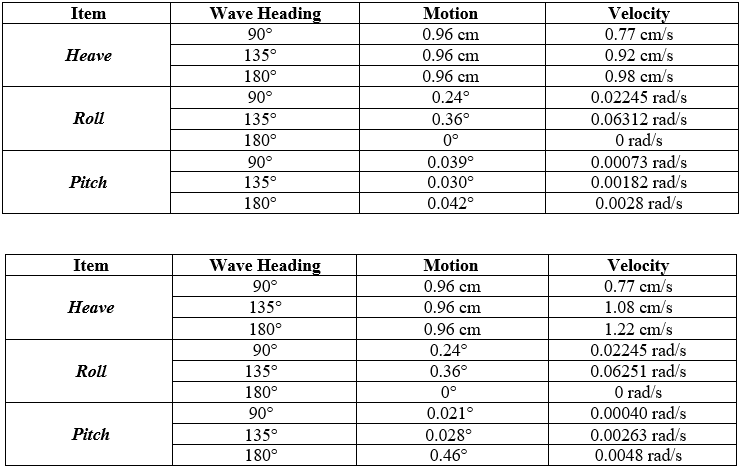
We did several tests by changing and combining the 3 test parameters that have been mentioned to get the best results for the reality of the ship's distance with the predetermined waypoints. The following is the data from the M8N GPS sensor test for the Mandakini Neo ship
GPS sensor testing is done by comparing the use of a combination of parameters in running the ship automatically. The best average is obtained when using the 2 waypoint parameter with a speed throttle of 50% and a waypoint radius of 0 m, which is 121.6 cm with a specified waypoint distance and the worst results are using the 1 waypoint parameter with a speed throttle of 70% and a waypoint radius of 1 m. From all the data obtained, it can be concluded that the more waypoints the accuracy of the gps will be because the path to be traversed is clearer in direction than we use fewer waypoints, the smaller the speed and the smaller the waypoint radius, the better the gps accuracy will be due to the larger the waypoint. radius, the greater the range that can be reached by the GPS so that the waypoint distance determined by the vehicle will be even further away. the best results in this trial will be applied to the use of each mission that will be carried out